Have you ever wondered how Facebook suggests friends you may know or how Amazon recommends products that seem to be just what you were looking for? The secret sauce behind these seemingly magical suggestions is often a graph database.
Unlike the spreadsheets or tables you might be used to, graph databases excel at handling data that’s all about connections, making them incredibly powerful for certain types of tasks.
Let’s demystify graph databases together. Imagine them as a vibrant city map where locations (data points) are connected by roads (relationships). Just as you’d find the best route from a coffee shop to a bookstore on a map, graph databases help find the most efficient paths and patterns in a network of data.
Whether it’s figuring out the quickest way to get from point A to point B or uncovering hidden patterns in data, graph databases offer a unique and powerful approach to managing and analyzing data.
Understanding Graph Databases: The Basics
At its core, a graph database is designed to store data in a graph structure, comprising nodes, edges, and properties. Nodes represent entities or objects, edges depict the relationships between these entities, and properties provide details about nodes and edges. This structure is inherently adept at illustrating complex relationships and patterns, making graph databases a go-to choice for scenarios where relationships are as critical as the data itself.
Why Choose Graph Databases?
Graph databases shine in contexts where connections between data points are paramount. They offer:
- Efficiency: Swiftly traverses connected data, which is cumbersome in relational databases.
- Flexibility: Adapts to schema changes with ease, accommodating evolving data models.
- Insightful: Uncovers patterns and relationships in data that might remain obscured in other database types.
Real-World Applications: Graph Databases in Action
The versatility of graph databases is evident across various sectors:
- Social Networks: They map user connections, interests, and activities, enhancing recommendations and content relevance.
- Fraud Detection: Financial institutions leverage graph databases to detect intricate fraud patterns and suspicious activities.
- Healthcare: They facilitate research by linking disparate data points, aiding in breakthrough discoveries.
A Closer Look at a Graph Database Example
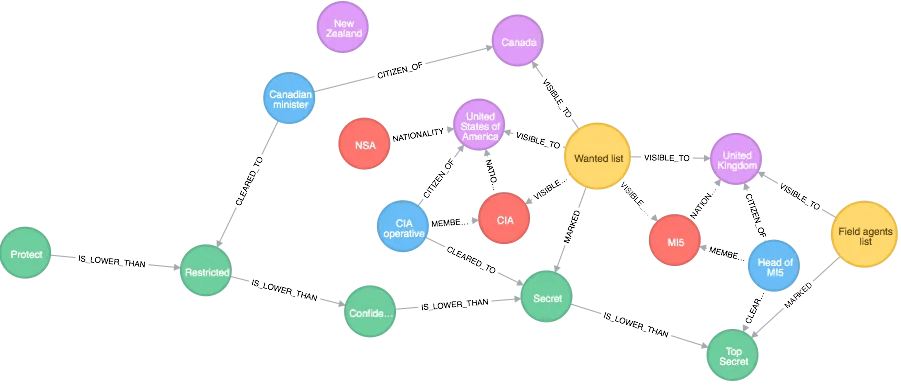
Consider a social networking site. A graph database can store users as nodes, relationships (friends, followers) as edges, and user attributes (age, interests) as properties. This structure allows for effective analysis of social connections, interest-based clustering, and targeted content delivery.
Choosing the Right Graph Database
Selecting an appropriate graph database hinges on specific project requirements. Here are key factors to consider:
- Scalability: Can the database handle your growing data and query complexity?
- Query Language: Is the query language intuitive and powerful enough for your needs?
- Community and Support: A robust community and professional support can significantly ease implementation and troubleshooting.
Graph Databases vs. Traditional Databases: Making the Choice
While graph databases excel in managing connected data, they’re not a one-size-fits-all solution. For applications where relationships aren’t a focal point, traditional databases might suffice. It’s crucial to assess your data structure and query needs to make an informed decision.
Implementing Graph Databases: Best Practices
To harness the full potential of graph databases, adhere to these guidelines:
- Data Modeling: Craft your model focusing on relationships. Understand the connections in your data to optimize your graph’s structure.
- Query Optimization: Leverage the strengths of graph queries. Utilize indexing and avoid overly broad search parameters.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitor performance and update your database to maintain efficiency and integrity.
Future Trends: The Evolving Graph Database Technology
Graph databases are on a trajectory of growth, driven by the increasing complexity and interconnectedness of data. Emerging trends include:
- Integration with AI and ML: Enhancing predictive analytics and machine learning models with rich, connected data from graph databases.
- Cloud-based Solutions: Cloud platforms offering managed graph database services for scalability and flexibility.
Enhancing User Experience with Graph Databases
Graph databases don’t just crunch numbers and connect data points; they significantly enhance user experiences across various digital platforms. By understanding and leveraging the intricate web of user preferences, behaviors, and interactions, graph databases empower applications to deliver personalized and contextually relevant experiences.
Personalization at Scale
Imagine logging into a music streaming service and being greeted with song recommendations that feel tailor-made for your taste. Or consider an e-commerce platform that knows your shopping preferences better than you do. Graph databases make this level of personalization possible by analyzing your past interactions, preferences, and even your network’s behavior.
- Content Recommendation: By mapping user preferences and historical interactions, platforms can suggest content that resonates with individual tastes, increasing engagement and user satisfaction.
- Dynamic User Interfaces: Apps can adjust their interfaces based on user behavior patterns identified through graph databases, making the user experience more intuitive and fluid.
Enhancing Search Functionality
Search engines and in-app search functionalities become significantly more powerful with graph databases. They can interpret the context of queries, understand relationships between different search terms, and deliver results that are more accurate and relevant to the user’s intent.
- Contextual Understanding: Graph databases can grasp the context behind a search query, allowing for more nuanced and accurate search results.
- Predictive Search: By analyzing patterns and connections in past search data, graph databases can anticipate user needs, offering predictive search suggestions that are often surprisingly on point.
Graph Databases Driving Innovation in Various Industries
The adaptability and power of graph databases have found applications in a multitude of industries, driving innovation and offering solutions to age-old challenges.
Financial Services: Combating Fraud
In the financial sector, graph databases are revolutionizing fraud detection. They can uncover complex patterns and hidden relationships among transactions that might indicate fraudulent activity, something that traditional databases might miss.
- Real-Time Fraud Detection: Graph databases can analyze transactions in real time, identifying suspicious patterns and connections swiftly to prevent fraud before it occurs.
- Network Analysis: By mapping the network of transactions, graph databases help financial institutions see the big picture, spotting anomalies and trends indicative of fraudulent networks.
Healthcare: Advancing Research and Patient Care
The healthcare industry benefits immensely from graph databases, from enhancing patient care to advancing medical research.
- Patient Data Analysis: Graph databases can integrate and analyze diverse patient data, providing a comprehensive view that aids in personalized care and treatment plans.
- Medical Research: By connecting disparate research data, graph databases can uncover new insights, accelerating medical breakthroughs and the development of new treatments.
Supply Chain and Logistics: Optimizing Operations
Graph databases are transforming supply chain management and logistics, making operations more efficient and responsive.
- Route Optimization: They can analyze and optimize routes in real time, considering various factors like traffic, weather, and delivery windows, ensuring efficient logistics operations.
- Supply Chain Visibility: By mapping the entire supply chain network, graph databases offer unprecedented visibility, helping companies anticipate disruptions and respond proactively.
Conclusion: The Impact of Graph Databases on Data Management
Graph databases offer a transformative approach to managing and analyzing interconnected data. By embracing this technology, organizations can gain deeper insights, enhance efficiency, and drive innovation. Whether it’s social networking, fraud detection, or complex data analysis, graph databases provide a robust framework for understanding the intricate tapestry of relationships in data.
Embarking on the graph database journey requires careful consideration of your data’s nature and your organization’s needs. By selecting the right graph database, adhering to best practices, and staying attuned to evolving trends, you can unlock the full potential of your data, gaining a competitive edge in the data-driven landscape.
Ben is a full-time data leadership professional and a part-time blogger.
When he’s not writing articles for Data Driven Daily, Ben is a Head of Data Strategy at a large financial institution.
He has over 12 years’ experience in Banking and Financial Services, during which he has led large data engineering and business intelligence teams, managed cloud migration programs, and spearheaded regulatory change initiatives.